In this tutorial by Professor Keith Williams, you will learn how to use predefined environments (Docker) to support a website, as well as basic skills of the command line. You need to finish all the assignments, and the tutorials listed below can guide you. Take screenshots of the results as the proof of your achievements.
Why should you learn about Docker?
Many developers are struggling with the deployment of their programs. Sometimes it is easy to deliver a program, but to deliver the running environment for that program is not that easy. Docker is the delivery of environments, and we can also use these predefined environments to run specific programs, such as Ubuntu and Apache (a server end program). Docker is a sort of flexible “virtual machine”, providing the minimum environment for your programs, and the environment has little relationship with the host/local physical machine.
Why should you learn about command line?
In most occasions of maintaining servers, there is no Graph User Interface (GUI), and the command line is the only way to interact with the server and the programs. So developers need to learn command line. In addition, the command line is efficient for professionals who need to conduct similar operations many times. For example, in Ubuntu, you can use “ls” to list files in the current directory, and use “cd” to change the present working directory. In vi, “q” command is used to quit the current file.
Tutorial resources and key steps:
1. Install Docker Engine
https://docs.docker.com/engine/install/
https://docs.docker.com/get-docker/
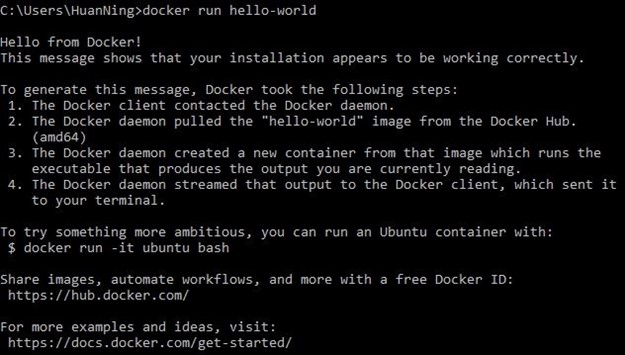
Key-step: After the installation, you can run “docker run hello-world” to test your installation. Below is a screenshots when run this command successfully on Windows OS.
2. Pull an Ubuntu image from Dockerhub.
https://docs.docker.com/engine/reference/commandline/pull/
Key-step 1: After logging into Docker, you can run “docker pull ubuntu” in your command line window.

Key-step 2: Use “docker images” to check existing Docker images on your computer.

3. How To Commit Changes To A Docker Image With Examples
https://phoenixnap.com/kb/how-to-commit-changes-to-docker-image
Note: Parameter “-it” of Docker brings you an interactive shell to communicate with the “virtual machine”.
Key-step 1: Run the Ubuntu image to start a Docker container, then log into this Ubuntu container:
Command: docker run -it ubuntu:latest /bin/bash

The container ID is “1ee65e9d5595” in the screenshot.
Key-step 2: Install applications in this Ubuntu container.
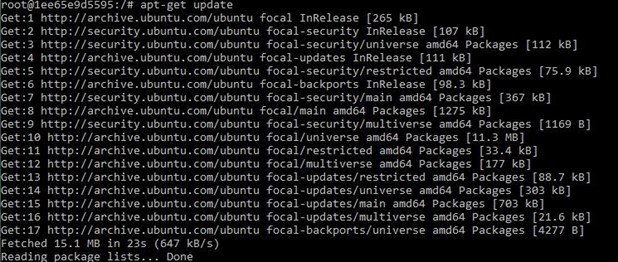
1) Update system using“apt-get update”.
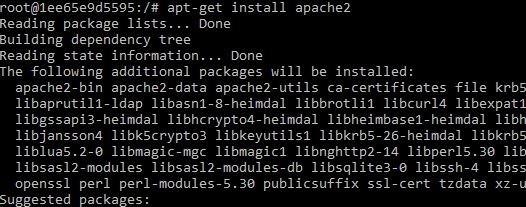
2) Install apache2 using “apt-get install apache2”.
3) Install vim text editor using “apt-get install vim”.

Key-step 3:Exit Ubuntu container.
1) Use command “exit”.
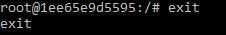
Key-step 4: Commit container to create a new Docker image.
1) Check the container using “docker ps -a”

2) Create a new Docker image using “docker commit 1ee65e9d5595 ubuntu-my_apache2”. “1ee65e9d5595” is the container ID and “ubuntu-my_apache2” is the name of a new Docker image.

3) Check the news images using “docker images”.

4. Docker Basics: How to Share Data Between a Docker Container and Host
https://thenewstack.io/docker-basics-how-to-share-data-between-a-docker-container-and-host/
Using command “docker run -it -p 127.0.0.1:80:80 -v H:\Docker_tutorial\local_dir:/var/www/html ubuntu-my_apache2 /bin/bash”.
Parameter explanation:
1) -it: log into an interactive shell
2) -p: expose an port of Docker container.
3) -v: bind a host directory to Docker container. “H:\Docker_tutoiral\local_dir” is a directory of the host computer, and “/var/www/htm” is the default location for the entry webpage of a website. Usually we put “index. Html” is this directory.

5. vi Editor in UNIX
https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/vi-editor-unix/
Vi index.html
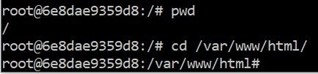
Key step 1: check the present working directory using “pwd” then go the html directory “/var/www/htm” using “cd /var/www/html”
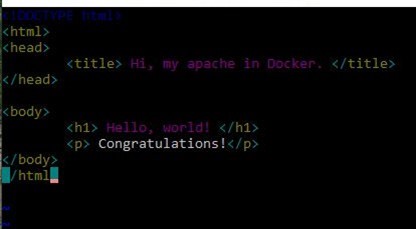
Key step 2: create an “index.html” file using “vi index.html”. Press “i” key to edit the new “index. Html” file. You can see “-- INSERT --” in the bottom of the command window, which means you can type html source code now. Try the shortcuts of vi to edit your file.

After finishing your “index.html” file, press the “ESC” key of your computer then type “:wq” to write the file and then quit vi.
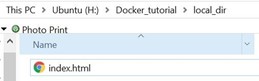
Meanwhile, you can find your “index.html” in your bind directory on your computer.
6. How to use Docker to host a website.
1) How To Start, Stop, Or Restart Apache Server On Ubuntu
https://phoenixnap.com/kb/ubuntu-start-stop-restart-apache
2) How to Run a Web Server from a Docker Container? Yes, I Know IT ! Ep 16
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=okw7fOYHSeI
3) Learn Docker in 12 Minutes
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YFl2mCHdv24
Key step 1: Start apache service using “/etc/init.d/apache2 restart” in your Docker container.

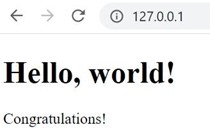
Using a browser of you host computer to access “127.0.0.1”, then you can see your website!